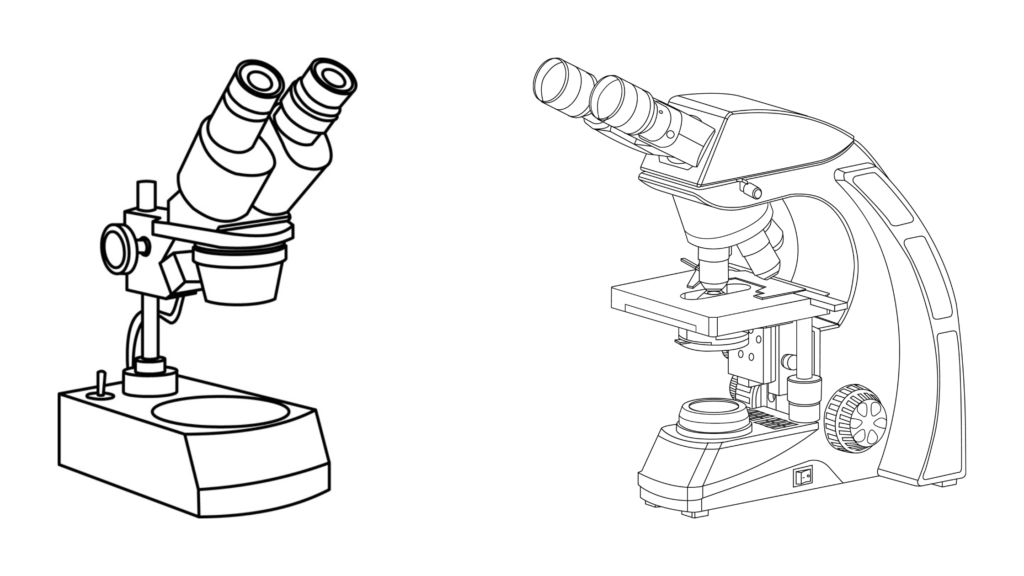
In the realm of microscopy, two popular instruments stand out: the binocular microscope and the stereo microscope. Each offers unique features and benefits, catering to different needs and applications. Let’s dive into a comprehensive comparison of these two powerful tools.
Binocular Microscope:
A binocular microscope, also known as a compound microscope, is a versatile tool widely used in laboratories, educational institutions, and research facilities.
Binocular Microscope Price:
Binocular microscopes vary in price depending on their specifications and intended use. Entry-level models can be found for as low as $100, while high-end professional models may cost several thousand dollars.
Uses of Binocular Microscope:
Binocular microscopes are essential for various scientific disciplines, including biology, medicine, forensics, and material sciences. They enable users to observe microscopic specimens with high magnification and clarity, making them invaluable for research and analysis.
Binocular Microscope Parts:
Key components of a binocular microscope include the eyepieces, objective lenses, stage, condenser, and light source. These parts work together to magnify and illuminate the specimen, allowing for detailed observation and analysis.
Binocular Microscope Principle:
The principle behind a binocular microscope involves the use of two sets of lenses (ocular and objective) to magnify the specimen. Light passes through the specimen, is refracted by the objective lenses, and is further magnified by the ocular lenses, producing a highly detailed image.
Read Also: What Is the Difference Between Compound & Binocular Microscope?
Stereo Microscope:
Unlike the binocular microscope, the stereo microscope offers a three-dimensional view of the specimen, making it ideal for tasks that require depth perception and manipulation.
Stereo Microscope Price:
Stereo microscopes come in a wide range of prices, with basic models starting at around $200 and advanced models costing upwards of $5000 or more.
Stereo Microscope Uses:
Stereo microscopes find applications in fields such as electronics, manufacturing, quality control, and dissection. Their ability to provide a 3D view of objects makes them indispensable for tasks that require precise inspection and manipulation.
Stereo Microscope Parts and Functions:
Key components of a stereo microscope include the eyepieces, objective lenses, zoom knob, focus knob, stage, and illumination system. These parts work together to provide a magnified, three-dimensional view of the specimen, allowing users to examine its structure and features in detail.
Read Also: What Is a Binocular Microscope – All Essential Things to Know
Principle of Stereo Microscope:
The principle behind a stereo microscope involves using two separate optical paths to create a three-dimensional image of the specimen. This is achieved by capturing two slightly different views of the specimen and presenting them to the observer’s eyes, mimicking the natural depth perception of human vision.
In conclusion, both the binocular microscope and the stereo microscope offer valuable insights into the microscopic world. While the binocular microscope excels in high-magnification, two-dimensional imaging, the stereo microscope provides a three-dimensional perspective, making it suitable for tasks that require depth perception and manipulation. Ultimately, the choice between the two depends on the specific requirements of the user and the intended application.
Read Also:
Introduction to Microscopy | Binocular Compound Microscope
Best Stereo Microscopes for Studying Insects & More
What Is a Trinocular Stereo Microscope and Its Uses?
Stereo Microscope Vs. Compound Microscope: a Beginner’s Guide